# Send your Docker container logs to AWS Cloudwatch using logspout
Jul 2, 2016 3 minute readAs a general rule Docker containers print to the STDOUT anything that should be logged. This simple approach is nothing but powerful and extensive. Logspout is a lightweight container that forwards the logs of other containers running on the same server. It is built in an extensible way with support for multiple log destinations. This guide will show how to configure Logspout-Cloudwatch to forward our logs to AWS CloudWatch.1
The instructions of this guide are based on Docker 1.9.
Step 1: Configure AWS Cloudwatch
We need an Access Key Id and a Secret Access Key that can forward logs to Cloudwatch. Here’s how to configure AWS Cloudwatch for Log Forwarders.
Step 2: Run the logspout-cloudwatch container
docker run -h $(hostname) \
-e "AWS_ACCESS_KEY_ID=xxxxxxxxxxxxxxxx" \
-e "AWS_SECRET_ACCESS_KEY=xxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxx" \
-e "LOGSPOUT=ignore" \
--volume=/var/run/docker.sock:/tmp/docker.sock --name=logspout \
--rm -it mdsol/logspout 'cloudwatch://us-east-1?DEBUG=1&NOEC2'
What is this?: Start and configure a container of the image mdsol/logspout. More details on the configuration can be found here.
Step 3: Run a container that generates logs
docker run \
-e "LOGSPOUT_GROUP=sample-docker-logs" \
ubuntu bash -c \
'for i in {1..10}; do echo "Hi, the date is $(date)" ; sleep 1; done'
What is this?: Start a container that will log the current date ten times and send its logs to the sample-docker-logs log group.
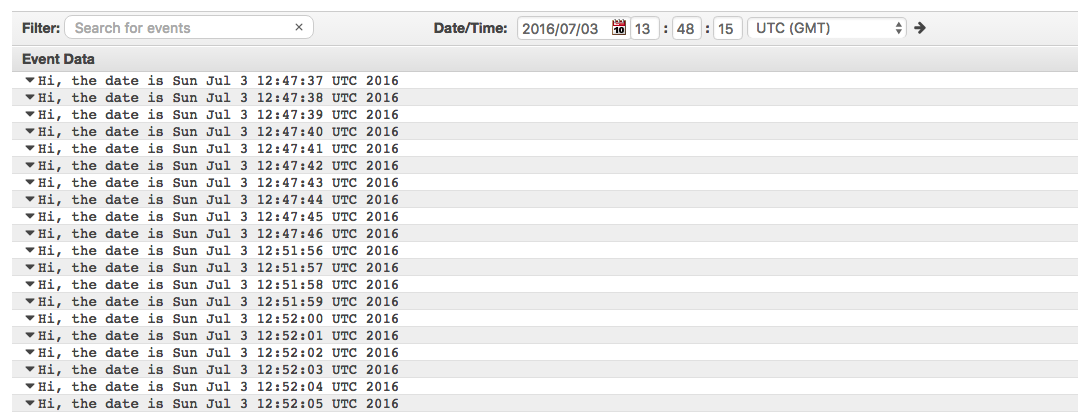
Step 4: Review the logs
1- Open the CloudWatch sample-docker-logs group
2- Click Search Events 
Your should be able to see your logs
Bonus: Docker Cloud configuration
Docker Cloud is a SaaS tool run by Docker to manage and automate container deployments. It is very powerful and yet simple to use. More info here.
1- Create and Start a logging Stack
logspout:
image: mdsol/logspout
deployment_strategy: every_node
autoredeploy: true
restart: on-failure
volumes:
- /var/run/docker.sock:/tmp/docker.sock
environment:
- AWS_ACCESS_KEY_ID=xxxxxxxxxxxxxxxx
- AWS_SECRET_ACCESS_KEY=xxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxx
- LOGSPOUT=ignore
command: 'cloudwatch://us-east-1?DEBUG=1&NOEC2'
What is this?: A Stack YAML file to configure a logspout service. Docker Cloud will deploy a mdsol/logspout container on every node under the account. Moreover, it will make sure our container gets restarted in case of a failure.
2- Create and Start hello-world Stack
helloworld:
image: ubuntu
target_num_containers: 1
environment:
- LOGSPOUT_GROUP=sample-docker-logs
command: bash -c 'for i in {1..10}; do echo "Hi, the date is $(date)" ; sleep 1; done'
-
Why Cloudwatch? Cloudwatch has excellent support for alerts and autoscaling. ↩